6. Meteorological input data#
Two formats for input meteorological forcing time series are accepted: at site data measured by weather stations and raster dataset generally coming from weather prediction or climatic models. Variables that may be configured in meteo configuration file, and related section name, are listed as follows:
precipitation with arbitrary time cumulation
[precipitation],daily cumulated precipitation
[precipitation-daily],subdaily air temperature averaged over arbitrary time
[temperature],daily averaged air temperature
[temperature-daily-mean],daily minimum air temperature
[temperature-daily-min],daily maximum air temperature
[temperature-daily-max],wind speed
[windspeed],solar radiation
[solar-radiation],air relative humidity
[relative-humidity].
When one section is missing (or commented out with # character) that
variable is not initialized in FEST simulation run. Definition of
precipitation with sub-daily or daily time cumulation in the same
simulation is useful when user needs to run simulation at sub-daily
time scale and, contemporary, export daily precipitation maps.
In this case daily cumulated precipitation does not affect
simulation results because it is only used for reporting purposes.
Definition of daily and subdaily air temperature in the same simulation is useful when user needs to run simulations that require different time discretization of input temperature. For instance this is the case when user is running a simulation with snow module activated that requires subdaily time step and has chosen the Hargreaves-Samani method to compute potential evapotranspiration that requires daily time step. In this case daily maximum and minimum air temperature are required as well.
No any global properties, i.e. out of any section, are required in this file.
Some features are common to all meteorological variables. Three interpolation methods are available:
Thiessen polygons (id = 1) [Thiessen, 1911]
Inverse distance weighting (IDW, id = 2)
Ordinary kriging (id = 3)
Interpolation method over a domain can be set in two ways. The first
way implies to use only one method all over the domain
(interpolation-assignment = 1) (Fig. 6.1).
In this case, interpolation method is set by interpolation
keyword (interpolation = 1 for Thiessen, interpolation = 2 for IDW, interpolation = 3 for kriging).
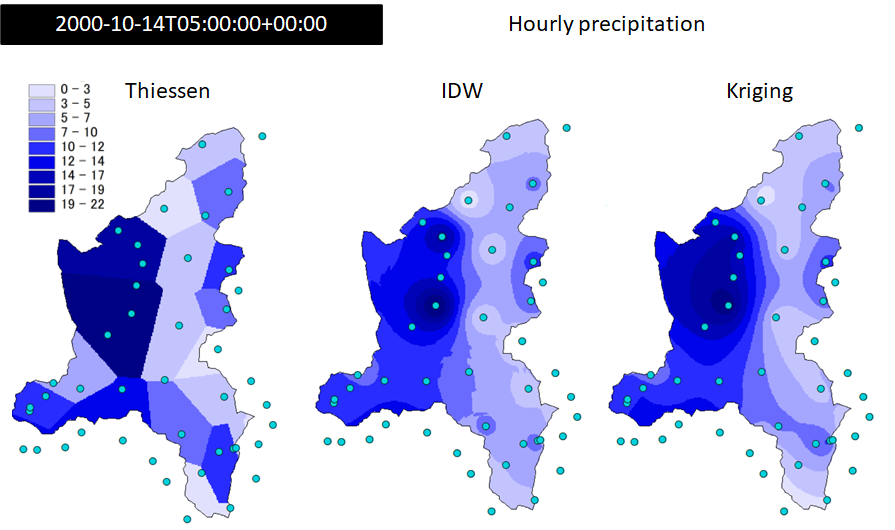
Fig. 6.1 Hourly precipitation data measured on 2000-10-14T05:00:00+00:00 over the Toce river basin (Italy) interpolated with Thiessen, IDW, and Kriging methods.#
A fourth option (interpolation = 0) is set when input data are provided
in forms of netCDF maps (for example coming from weather prediction models).
In this case there’s no need to interpolate site data but some adjustments
are applied by FEST in order to match spatial resolution and coordinate
reference system of the analysis (coordinate conversion and nearest
neighbours sampling are used for these purposes).
The second way to interpolate station data implies to use a different
methods for each subareas of the domain (interpolation-assignment = 2)
(Fig. 6.2). In this case a map is provided (set in [[interpolation]] sub-section)
that sets for each cell the id of interpolation method among the three available
(1 = Thiessen, 2 = IDW, 3 = Kriging). Virtually every cell may have an interpolation
method associated that differs from the ones of the surrounding cells.
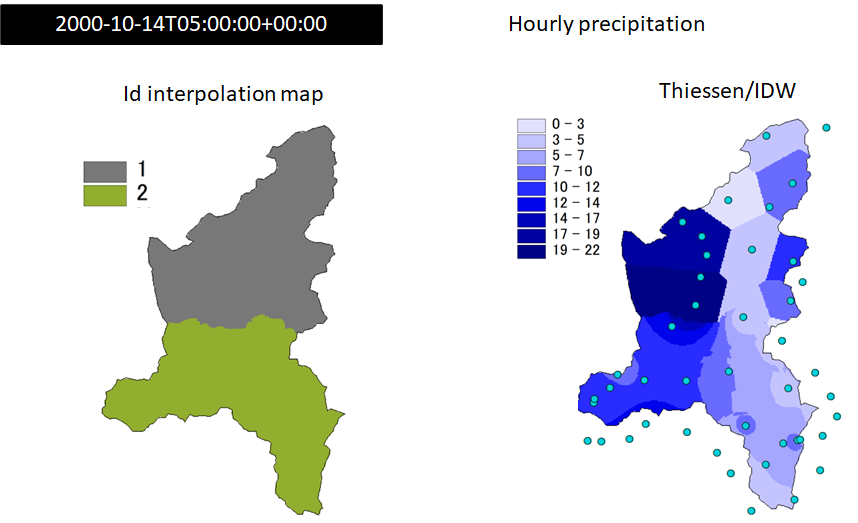
Fig. 6.2 Hourly precipitation data measured on 2000-10-14T05:00:00+00:00 over the Toce river basin (Italy) interpolated with Thiessen (id = 1) and IDW (id = 2). Left map shows spatial distribution of interpolation Id.#
When an interpolation method is activated, whether by an id map or by interpolation = keyword,
specific parameters may be required or set as option by the user.
Meteorological maps can be exported to files by setting export = 1.
6.1. Precipitation with arbitrary time cumulation#
This section is defined by [precipitation] in meteo configuration file. Unit of input
data is mm cumulated in dt. The definitions of the keywords are reported in Table 6.1.
Where not specified as MANDATORY, keywords are assumed to be optional.
Keyword |
Description |
Requirements |
|---|---|---|
|
map with interpolation method codes |
Used when |
|
Map (or series of maps in netcdf format) used to assign lapse rate |
CRS and spatial resolution must be the same of mask |
|
Cumulation time [s] |
Integer greater than 0. MANDATORY |
|
Option to apply elevation based correction (lapse rate) |
1 = use elevation to interpolate (requires definition of |
|
activate grid exporting |
1 = export interpolated grid, 0 = do not export interpolated grid MANDATORY |
|
time between two exportations (s) |
Integer greater than 0 |
|
epsg of coordinate reference system of exported grid |
Integer. List of accepted values in Section 1.2 |
|
1 = esri_ascii, 2 = esri_binary, 3 = netcdf |
Integer among 1-3 |
|
folder where to put exported grids |
string |
|
time and date to start exporting |
Date and time according to the International Standard ISO 8601 specifications |
|
time and date to stop exporting |
Date and time according to the International Standard ISO 8601 specifications |
|
File that contains data to read |
MANDATORY |
|
power to be used with idw, |
When missing, default = 2. |
|
Interpolation method when interpolation-assignment = 1 |
1 = thiessen, 2 = inverse distance weight (idw), 3 = kriging, 0 = read interpolated field |
|
Defines the way of interpolation |
1 = one method for the entire domain, 2 = a map with interpolation method codes assigned by subsection |
|
Wheter to include anisotropy when fitting semivariogram model |
1 = considers anisotropy, default = 0 excludes anisotropy |
|
number of lag bins for semivariogram |
if undefined or set to 0 default to 15 |
|
Limit distance (m) to be considered for semivariogram assessment |
If undefined or set to 0, it is computed automatically |
|
Option to export to file variance map associated to kriging interpolation |
Set to 1 to export variance, 0 to suppress it. When missing Default = 0 |
|
Semivariogram model to fit for kriging interpolation. When automatic fitting is chosen, the best among spherical and exponential is chosen. |
1 = spherical, 2 = exponential, 3 = gaussian, 0 = automatic fitting. default to 2 |
|
Method to assign lapse rate for elevation based correction |
1 = one scalar for the entire domain, 2 = a map that may change in time. Requires the definition of subsection |
|
Lapse rate to use for elevation based correction (mm/m) |
Real number greater than 0 when variable increase with elevation |
|
number of nearest points to be considered for interpolation |
Mandatory for kriging and idw |
|
Add an offset (mm) |
Real number greater than zero if variable increase is required, lower than zero if decrease is required. |
|
Apply a scale factor (multiplicative). May be used for unit conversion or for model calibration. It is applied after elevation based correction |
real number, optional |
|
Standard name of variable to be read in netcdf file |
|
|
minimum percentage of valid data that must be prresent to consider valid the aggregated value, when data from several time steps are read. |
Percentage (0-1). When it is missing default is 1 that means that all values have to be valid to compute aggregation. |
|
Name of variable to be read in netcdf file |
|
The following example uses the minimum number of mandatory keys. It sets the
interpolation of data from the file precipitation.txt using Thiessen polygon
method without drift and grid exportation.
[precipitation]
dt = 3600
file = ./meteo/precipitation.txt
interpolation-assignment = 1
interpolation = 1
elevation-drift = 0
export = 0
The next example requires to interpolate data using Kriging without anisotropy.
Variogram model is automatically chosen, and number of lags, and maximum distance
to be considered for semi-variogram assessment are computed automatically, as well.
Elevation drift is used during interpolation, with a lapse rate of 0.01 mm/h/m.
Interpolated maps of precipitation and variance are exported hourly in NetCDF
format in subfolder ./results/precipitation_grid, from date 2014-07-07T00:00:00+00:00 to date 2014-07-10T00:00:00+00:00.
[precipitation]
dt = 3600
file = ./meteo/precipitation.txt
interpolation-assignment = 1
interpolation = 3
kriging-variance = 1
kriging-anisotropy = 0
kriging-variogram-model = 0
kriging-lags = 0
kriging-maxlag = 0
elevation-drift = 1
lapse-rate-assignment = 1
lapse-rate-scalar = 0.01
export = 1
export-path = ./results/precipitation_grid
export-start = 2014-07-07T00:00:00+00:00
export-stop = 2014-07-10T00:00:00+00:00
export-dt = 3600
export-format = 3
export-epsg = 3003
6.2. Daily precipitation#
Daily precipitation properties are set in section [precipitation-daily].
This section is similar to [precipitation] section except dt that is not required.
Having both [precipitation] and [precipitation-daily] configured in one simulation
is useful when user needs to run simulation at sub-daily time scale and, at
the same time, export daily precipitation maps.
6.3. Subdaily air temperature averaged over arbitrary time#
This section is defined by [temperature] in meteo configuration file. Unit of
input data is degree Celsius. Degree Kelvin data can be used as long as offset
is applied in order to convert data to degree Celsius unit (see examples below).
The definitions of the keywords are reported in Table 6.2. Where not
specified as MANDATORY, keywords are assumed to be optional. Setting occurs
similarly to precipitation data. A specific option of temperature data,
not available in precipitation section for example, is set in order to
compute vertical lapse rate from station data.
Keyword |
Description |
Requirements |
|---|---|---|
|
map with interpolation method codes |
Used when |
|
Map (or series of maps in netcdf format) used to assign lapse rate |
CRS and spatial resolution must be the same of mask |
|
Cumulation time [s] |
Integer greater than 0. MANDATORY |
|
Option to apply elevation based correction (lapse rate) |
1 = use elevation to interpolate (requires definition of |
|
activate grid exporting |
1 = export interpolated grid, 0 = do not export interpolated grid MANDATORY |
|
time between two exportations (s) |
Integer greater than 0 |
|
epsg of coordinate reference system of exported grid |
Integer. List of accepted values in Section 1.2 |
|
1 = esri_ascii, 2 = esri_binary, 3 = netcdf |
Integer among 1-3 |
|
folder where to put exported grids |
string |
|
time and date to start exporting |
Date and time according to the International Standard ISO 8601 specifications |
|
time and date to stop exporting |
Date and time according to the International Standard ISO 8601 specifications |
|
File that contains data to read |
MANDATORY |
|
power to be used with idw, |
When missing, default = 2. |
|
Interpolation method when |
1 = thiessen, 2 = inverse distance weight (idw), 3 = kriging, 0 = read interpolated field |
|
Defines the way of interpolation |
1 = one method for the entire domain, 2 = a map with interpolation method codes assigned by subsection |
|
Wheter to include anisotropy when fitting semivariogram model |
1 = considers anisotropy, default = 0 excludes anisotropy |
|
number of lag bins for semivariogram |
if undefined or set to 0 default to 15 |
|
Limit distance (m) to be considered for semivariogram assessment |
If undefined or set to 0, it is computed automatically |
|
Option to export to file variance map associated to kriging interpolation |
Set to 1 to export variance, 0 to suppress it. When missing Default = 0 |
|
Semivariogram model to fit for kriging interpolation. When automatic fitting is chosen, the best among spherical and exponential is chosen. |
1 = spherical, 2 = exponential, 3 = gaussian, 0 = automatic fitting. default to 2 |
|
Method to assign lapse rate for elevation based correction |
1 = one scalar for the entire domain, 2 = a map that may change in time. Requires the definition of subsection |
|
Option to set wether to compute lapse rate from station data or use the assigned value |
1 = compute lapse rate from data at each time step, 0 = use assigned lapse rate. Requires the definition of r2min |
|
Lapse rate to use for elevation based correction (mm/m) |
Real number greater than 0 when variable increase with elevation |
|
Number of nearest points to be considered for interpolation |
Mandatory for kriging and idw |
|
Adds an offset (degree Celsius) |
Real number greater than zero if variable increase is required, lower than zero if decrease is required. |
|
Value of linear regression R² below which value set by lapse-rate-scalar is used instead of computed lapse rate |
Real number in the range 0-1 |
|
Apply a scale factor (multiplicative). May be used for unit conversion or for model calibration. It is applied after elevation based correction |
real number, optional |
|
Standard name of variable to be read in netcdf file |
|
|
minimum percentage of valid data that must be prresent to consider valid the aggregated value, when data from several time steps are read. |
Percentage (0-1). When it is missing default is 1 that means that all values have to be valid to compute aggregation. |
|
Name of variable to be read in netcdf file |
|
The following example reads temperature data (unit degree Kelvin) from file temperature.txt in meteo subfolder (note the relative path notation) by averaging over 12 hours time span (43200 s). So, assuming that data are stored in temperature.txt file with hourly time step, each time a new reading is performed, 12 data are read and averaged. In case nodata values are encountered, if less than 60% of data are valid numbers (valid-threshold = 0.6), the resulting value is set as nodata. Data are interpolated with inverse distance weighting algorithm (interpolation = 2) with power of distance 2 (idw-power = 2.) and considering 15 nearest stations (nearest-points = 15). An elevation drift is applied (elevation-drift = 1) with lapse rate computed from data (lapse-rate-computation = 1). If the coefficient of determination of the linear regression applied to compute the lapse rate is less than 0.6 (r2min = 0.6), the value -0.0065 °C/m is used as lapse rate instead (lapse-rate-scalar = -0.0065). An offset of -273.15 °C is applied in order to convert map from degree Kelvin to degree Celsius (offset = -273.15).
[temperature]
dt = 43200
file = ./meteo/temperature.txt
valid-threshold = 0.6
interpolation-assignment = 1
interpolation = 2
idw-power = 2.
nearest-points = 15
elevation-drift = 1
lapse-rate-computation = 1
r2min = 0.6
lapse-rate-scalar = -0.0065
offset = -273.15
export = 0
6.4. Daily mean air temperature#
Daily mean air temperature properties are set in section [temperature-daily-mean].
This section is similar to [temperature] section except dt that is not required.
Having both [temperature] and [temperature-daily-mean] configured in one simulation
is useful when different processes require air temperature data with different time span.
For example, computation of evapotraspiration with Hargreaves-Samani equation requires
daily mean, minimum and maximum air temperature, and in the same simulation hourly
air temperature is required to simulate snow melt and accumulation.
6.5. Daily minimum air temperature#
Daily minimum air temperature properties are set in section [temperature-daily-min].
This section is similar to [temperature] section except dt that is not required.
Having both [temperature] and [temperature-daily-min] configured in one simulation
is useful when different processes require air temperature data with different time span.
For example, computation of evapotraspiration with Hargreaves-Samani equation requires
daily mean, minimum and maximum air temperature, and in the same simulation hourly air
temperature is required to simulate snow melt and accumulation.
6.6. Daily maximum air temperature#
Daily maximum air temperature properties are set in section [temperature-daily-max].
This section is similar to [temperature] section except dt that is not required.
Having both [temperature] and [temperature-daily-max] configured in one simulation
is useful when different processes require air temperature data with different time span.
For example, computation of evapotraspiration with Hargreaves-Samani equation requires
daily mean, minimum and maximum air temperature, and in the same simulation hourly air
temperature is required to simulate snow melt and accumulation.
6.7. Solar radiation#
This section is defined by [solar-radiation] in meteo configuration file.
Unit of input data is W/m². The definitions of the keywords are reported in Table 6.3.
Where not specified as MANDATORY, keywords are assumed to be optional.
Keyword |
Description |
Requirements |
|---|---|---|
|
map with interpolation method codes |
Used when |
|
Cumulation time [s] |
Integer greater than 0. MANDATORY |
|
Option to apply topographic drift |
1 = use elevation to interpolate, 0 = no, If missing, default = 0 |
|
activate grid exporting |
1 = export interpolated grid, 0 = do not export interpolated grid MANDATORY |
|
time between two exportations (s) |
Integer greater than 0 |
|
epsg of coordinate reference system of exported grid |
Integer. List of accepted values in Section 1.2 |
|
1 = esri_ascii, 2 = esri_binary, 3 = netcdf |
Integer between 1-3 |
|
folder where to put exported grids |
string |
|
time and date to start exporting |
Date and time according to the International Standard ISO 8601 specifications |
|
time and date to stop exporting |
Date and time according to the International Standard ISO 8601 specifications |
|
File that contains data to read |
MANDATORY |
|
power to be used with idw, |
When missing, default = 2. |
|
Interpolation method when interpolation-assignment = 1 |
1 = thiessen, 2 = inverse distance weight (idw), 3 = kriging, 0 = read interpolated field |
|
Defines the way of interpolation |
1 = one method for the entire domain, 2 = a map with interpolation method codes assigned by subsection |
|
Wheter to include anisotropy when fitting semivariogram model |
1 = considers anisotropy, default = 0 excludes anisotropy |
|
number of lag bins for semivariogram |
if undefined or set to 0 default to 15 |
|
Limit distance (m) to be considered for semivariogram assessment |
If undefined or set to 0, it is computed automatically |
|
Option to export to file variance map associated to kriging interpolation |
Set to 1 to export variance, 0 to suppress it. When missing Default = 0 |
|
Semivariogram model to fit for kriging interpolation. When automatic fitting is chosen, the best among spherical and exponential is chosen. |
1 = spherical, 2 = exponential, 3 = gaussian, 0 = automatic fitting. default to 2 |
|
number of nearest points to be considered for interpolation |
Mandatory for kriging and idw |
|
Add an offset (mm) |
Real number greater than zero if variable increase is required, lower than zero if decrease is required. |
|
Apply a scale factor (multiplicative). May be used for unit conversion or for model calibration. It is applied after elevation based correction |
real number, optional |
|
Standard name of variable to be read in netcdf file |
|
|
Time zone (unit = hour) of local time. |
Mandatory when elevation-drift = 1 |
|
minimum percentage of valid data that must be prresent to consider valid the aggregated value, when data from several time steps are read. |
Percentage (0-1). When it is missing default is 1 that means that all values have to be valid to compute aggregation. |
|
Name of variable to be read in netcdf file |
|
The next example requires to interpolate station ovservations from file RADD_2000-01-01_2011-12-31.fts using
inverse distance with power 1.5 and 15 closest stations. Elevation drift is applied using 1 hour as time zone to compute local time.
[solar-radiation]
dt = 3600
file = ./meteo/RADD_2000-01-01_2011-12-31.fts
interpolation-assignment = 1
interpolation = 2
idw-power = 1.5
nearest-points = 15
elevation-drift = 1
time-zone = 1
export = 0
6.8. Air relative humidity#
This section is defined by [relative-humidity] in meteo configuration file. Unit
of input data is percentage in the range 0-100. Interpolation of relative humidity
data is similar to other meteorological variables except elevation drift that is
not available. Definitions of keywords are reported in Table 6.4. Where
not specified as MANDATORY, keywords are assumed to be optional.
Keyword |
Description |
Requirements |
|---|---|---|
|
map with interpolation method codes |
Used when |
|
Cumulation time [s] |
Integer greater than 0. MANDATORY |
|
activate grid exporting |
1 = export interpolated grid, 0 = do not export interpolated grid MANDATORY |
|
time between two exportations (s) |
Integer greater than 0 |
|
epsg of coordinate reference system of exported grid |
Integer. List of accepted values in Section 1.2 |
|
1 = esri_ascii, 2 = esri_binary, 3 = netcdf |
Integer between 1-3 |
|
folder where to put exported grids |
string |
|
time and date to start exporting |
Date and time according to the International Standard ISO 8601 specifications |
|
time and date to stop exporting |
Date and time according to the International Standard ISO 8601 specifications |
|
File that contains data to read |
MANDATORY |
|
power to be used with idw, |
When missing, default = 2. |
|
Interpolation method when interpolation-assignment = 1 |
1 = thiessen, 2 = inverse distance weight (idw), 3 = kriging, 0 = read interpolated field |
|
Defines the way of interpolation |
1 = one method for the entire domain, 2 = a map with interpolation method codes assigned by subsection |
|
Wheter to include anisotropy when fitting semivariogram model |
1 = considers anisotropy, default = 0 excludes anisotropy |
|
number of lag bins for semivariogram |
if undefined or set to 0 default to 15 |
|
Limit distance (m) to be considered for semivariogram assessment |
If undefined or set to 0, it is computed automatically |
|
Option to export to file variance map associated to kriging interpolation |
Set to 1 to export variance, 0 to suppress it. When missing Default = 0 |
|
Semivariogram model to fit for kriging interpolation. When automatic fitting is chosen, the best among spherical and exponential is chosen. |
1 = spherical, 2 = exponential, 3 = gaussian, 0 = automatic fitting. default to 2 |
|
number of nearest points to be considered for interpolation |
Mandatory for kriging and idw |
|
Add an offset (mm) |
Real number greater than zero if variable increase is required, lower than zero if decrease is required. |
|
Apply a scale factor (multiplicative). May be used for unit conversion or for model calibration. It is applied after elevation based correction |
real number, optional |
|
Standard name of variable to be read in netcdf file |
|
|
minimum percentage of valid data that must be prresent to consider valid the aggregated value, when data from several time steps are read. |
Percentage (0-1). When it is missing default is 1 that means that all values have to be valid to compute aggregation. |
|
Name of variable to be read in netcdf file |
|
The next example requires to interpolate station observations from
file relative_humidity.fts (in subfolder meteo) using interpolation
methods defined in map interpolation_id.asc. Assuming id 2 and 3 are
present in interpolation_id.asc, two interpolation methods are applied:
inverse distance with power 2 and 25 closest stations, and kriging by fitting
exponential semivariogram model (kriging-variogram-model = 2) with 15
lags (kriging-lags = 15) and maximum distance of 100000 m (kriging-maxlag = 100000).
Interpolated maps are exported hourly (export-dt = 3600) in ESRI ASCII format
(export-format = 1) from 2000-10-12T01:00:00+00:00 to 2000-10-16T23:00:00+00:00.
Maps are converted to Geodetic WGS84 coordinate reference system (export-epsg = 4326)
and are saved to ./results/humidity folder (export-path = ./results/humidity).
[relative-humidity]
dt = 3600.
file = ./meteo/relative_humidity.fts
interpolation-assignment = 2
idw-power = 2.
kriging-anisotropy = 0
kriging-variogram-model = 2
kriging-lags = 15
kriging-maxlag = 100000
valid-threshold = 1.0
nearest-points = 25
export = 1
export-path = ./results/humidity
export-start = 2000-10-12T01:00:00+00:00
export-stop = 2000-10-16T23:00:00+00:00
export-dt = 3600
export-format = 1
export-epsg = 4326
[[interpolation]]
file = ./dati/interpolation_id.asc
format = esri-ascii
epsg = 23032
6.9. Wind speed#
This section is defined by [wind-speed] in meteo configuration file. Unit of
input data is m/s. Besides Thiessen, inverse distance and kriging methods to
interpolate local measurements, two further methods are available for wind speed
data: Micromet algorithm developed by [Liston, 2006] and the method proposed
by [González-Longatt et al., 2015]. Both methods use topographic features like
terrain elevation, slope and curvature to drift interpolated wind speed.
Wind direction is required when one of these two methods is chosen. Unit
of wind direction data is degree (0-360 meteorological convention, the direction
from which wind originates). Definitions of keywords are reported in Table 6.5.
Where not specified as MANDATORY, keywords are assumed to be optional.
Keyword |
Description |
Requirements |
|---|---|---|
|
map with interpolation method codes |
Used when |
|
Cumulation time [s] |
Integer greater than 0. MANDATORY |
|
activate grid exporting |
1 = export interpolated grid, 0 = do not export interpolated grid MANDATORY |
|
time between two exportations (s) |
Integer greater than 0 |
|
epsg of coordinate reference system of exported grid |
Integer. List of accepted values in Section 1.2 |
|
1 = esri_ascii, 2 = esri_binary, 3 = netcdf |
Integer between 1-3 |
|
folder where to put exported grids |
string |
|
time and date to start exporting |
Date and time according to the International Standard ISO 8601 specifications |
|
time and date to stop exporting |
Date and time according to the International Standard ISO 8601 specifications |
|
File that contains data to read |
MANDATORY |
|
power to be used with idw, |
When missing, default = 2. |
|
Interpolation method when interpolation-assignment = 1 |
1 = thiessen, 2 = idw, 3 = kriging, 4 = micromet, 5 = gonzalez, 0 = read interpolated field |
|
Defines the way of interpolation |
1 = one method for the entire domain, 2 = a map with interpolation method codes assigned by subsection [[interpolation]]. MANDATORY |
|
Wheter to include anisotropy when fitting semivariogram model |
1 = considers anisotropy, default = 0 excludes anisotropy |
|
number of lag bins for semivariogram |
if undefined or set to 0 default to 15 |
|
Limit distance (m) to be considered for semivariogram assessment |
If undefined or set to 0, it is computed automatically |
|
Option to export to file variance map associated to kriging interpolation |
Set to 1 to export variance, 0 to suppress it. When missing Default = 0 |
|
Semivariogram model to fit for kriging interpolation. When automatic fitting is chosen, the best among spherical and exponential is chosen. |
1 = spherical, 2 = exponential, 3 = gaussian, 0 = automatic fitting. default to 2 |
|
Length scale [m] used to compute curvature when micromet methos is required |
If undefined default to 5000 m |
|
slope weighting factor used by micromet |
If undefined default value = 0.5 |
|
curvature weighting factor used by micromet |
If undefined default value = 0.5 |
|
number of nearest points to be considered for interpolation |
Mandatory for kriging and idw |
|
Add an offset (mm) |
Real number greater than zero if variable increase is required, lower than zero if decrease is required. |
|
Apply a scale factor (multiplicative). May be used for unit conversion or for model calibration. It is applied after elevation based correction |
real number, optional |
|
Standard name of variable to be read in netcdf file |
|
|
minimum percentage of valid data that must be prresent to consider valid the aggregated value, when data from several time steps are read. |
Percentage (0-1). When it is missing default is 1 that means that all values have to be valid to compute aggregation. |
|
Name of variable to be read in netcdf file |
|
|
File that contains wind direction data to read |
Required when Micromet or Gonzalez-Longatt methods are chosen |
The next example requires to interpolate station observations from file windspeed.fts
(in subfolder meteo) using interpolation methods defined in map interpolation_wind.asc.
Assuming id 2 and 4 are present in interpolation_wind.asc, two interpolation methods are
applied: inverse distance (id = 2) with power 2 (idw-power = 2.) and 5 closest stations
(nearest-points = 5), and Micromet (id = 4) with length scale 6000 m (micromet-length-scale = 6000.),
slope weighting factor = 0.6 (micromet-slopewt = 0.5) and curvature weighting factor = 0.4 (micromet-curvewt = 0.4).
[wind-speed]
dt = 3600
file = ./meteo/windspeed.fts
interpolation-assignment = 2
idw-power = 2.
micromet-length-scale = 6000.
micromet-slopewt = 0.5
micromet-curvewt = 0.5
wind-direction-file = ./meteo/winddirection.fts
valid-threshold = 1.0
nearest-points = 5
export = 0
[[interpolation]]
file = ./dati/interpolation_wind.asc
format = esri-ascii
epsg = 23032